ACL Rehabilitation
PROBLEM
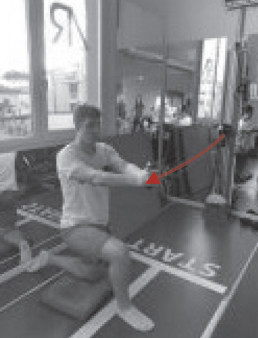
In the case of a patient facing an ACL rehabilitation; the whole rehab program was based on a specific path focusing on muscular reinforcement, using mainly the Desmotec D and V.
TREATMENT
During the first phases, Desmotec devices played a very important role in monitoring the patient’s progresses on shifting the load from healthy to operated limb, using D for balance and isometric tests, followed by exercises with specific strap on the V. The last phase of the rehab process was focused on achieving the complete leg extension, complete balance recovery and full load on the limb, using the V for functional movement equipped with a specific tool and isometric works.
RESULTS
Desmotec devices allowed the patient to overcome the temporal gap linked to re-conditioning, in full compliance with the physiological time previously estimated. Desmotec therefore allowed to re-evaluate the whole rehab preparatory linked to the functionality of the final gesture.
Would you like to know more about DESMOTEC technology, devices and training methods?
NeuroMuscolar Training on DLine in a subject with Parkinson' s disease to mantain strength and balance
This study explains the importance of neuromuscular training, also focusing on basic exercises of proprioception and a subject with Parkinson’s disease, to help the subject to maintain balance and strenght.
INTRODUCTION
Postural control requires a complex integration of motor performance and sensory perceptions.
Soft tissue injuries can adversely affect postural control, as well as mechanical stability and somatosensory function. This reduction in postural stability can therefore lead to a higher risk of secondary damage, resulting in a pathological cycle.
-
Thomas Bartels, Kay Brehme, Martin Pyschik, Stephan Schulze, Karl-Stefan Delank, Georg Fieseler, Kevin G. Laudner, Souhail Hermassi, René Schwesig, Pre- and postoperative postural regulation following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation 2018;14(1):143-151
-
Fulton J, Wright K, Kelly M, Zebrosky B, Zanis M, Drvol C, Butler R. Injury risk is altered by previous injury: a systematic review of the literature and presentation of causative neuromuscular factors. Int J Sports Phys Ther 2014;9:583-595.
-
Haas CT, Buhlmann A, Turbanski S, Schmidtbleicher D. Proprioceptive and sensorimotor performance in Parkinson’s disease. Res Sports Med 2006;14:273-287.
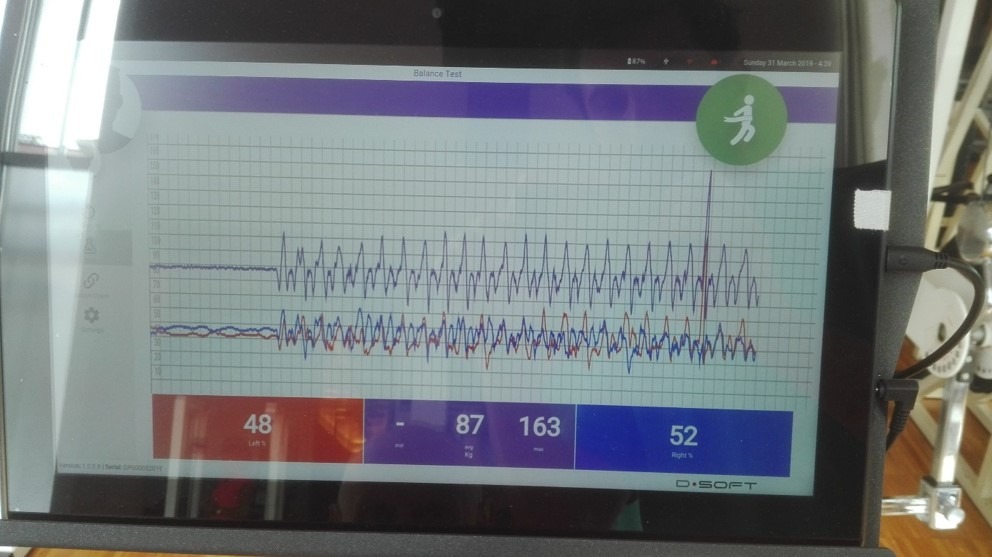
The correct load distribution between left and right foot is the basic exercise of proprioception. therefore, we decided to use the ‘balance test‘ function of the DLine Desmotec platform as a balancing feedback during the squat, to create a neuro-muscular exercise in patients with balance deficits.
PATIENT CARD
| Gender | Male |
| Age | 77 |
| LIFESTYLE | Cross Country Skiing |
PROBLEM: PTA left-rigth >10 y, low back pain, Parkinson’s disease
OBJECTIVE TO BE ACHIEVED: Maintenance of stength and balance
REHABILITATION PLAN
INSTRUMENTS:
- Reinforcement with isotonic machines
- Exercises on unstable plates
- Exercises for core stability
- To combine in a single exercise reinforcement and improvement of balance, we added the squat execution on the DLINE DESMOTEC platform
- The “balance test” program of the Desmotec software provides the patient with real-time visual feedback of the right-left foot balance
PROTOCOL
| Device | DLine |
| Test | Balance Test during Squat |
| Tool | — |
| Disc | — |
| Duration | 1 minute |
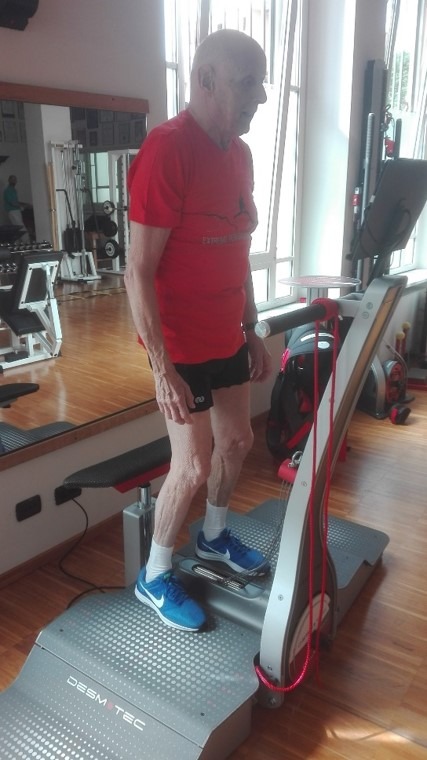

The patient is asked to position himself on the platform, with his feet equidistant from the center and instructed to take a minute of squat.
RESULTS
- The final report shows the therapist the quality of the task execution and provides the patient with feedback on the actual balance maintained
- The challenge to be offered to the patient is to maintain the two lines as similar as possible, and to have a numerical balance value close to 50/50
Benefits of using of Desmotec :
- The patient is facilitated in learning from visual feedback in real time
- The patient feels involved in the challenge, therefore appears motivated, despite the challenging task from the muscular point of view
- The therapist can monitor the correct execution of the gesture in real time